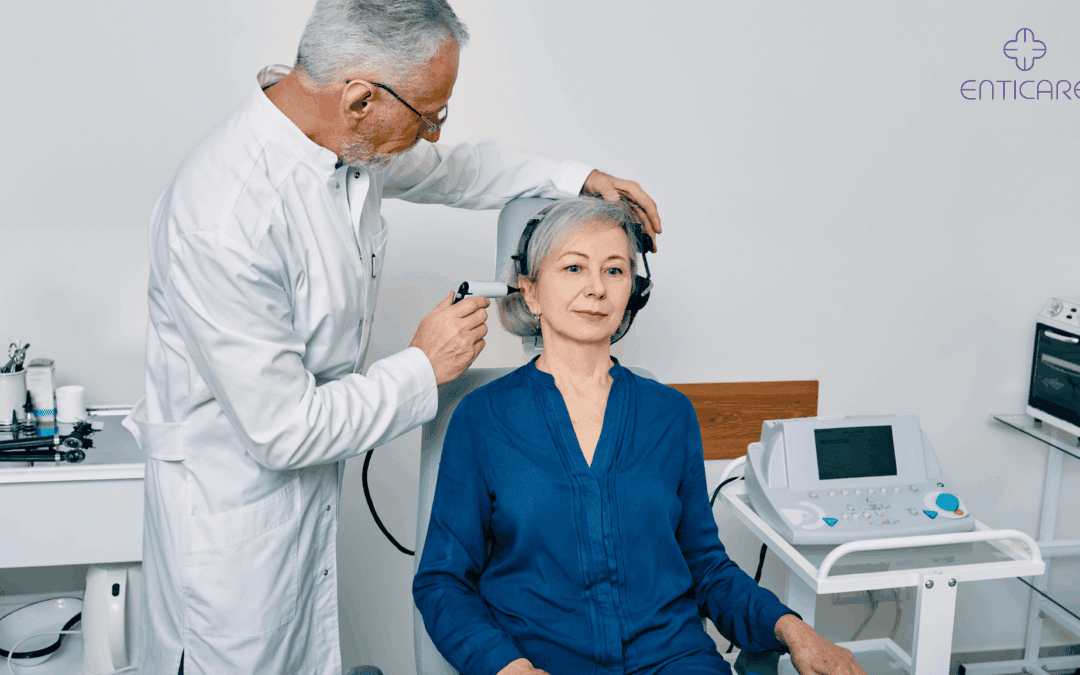
Hearing issues can be challenging, affecting your daily life and relationships. Knowing which type of hearing professional to see can significantly affect how quickly and effectively you address these issues. But with terms like “audiologist,” “ENT,” “otologist,” and “hearing instrument specialist” floating around, understanding who to consult can be confusing. Here’s a guide to the different types of hearing doctors and when to seek their expertise.
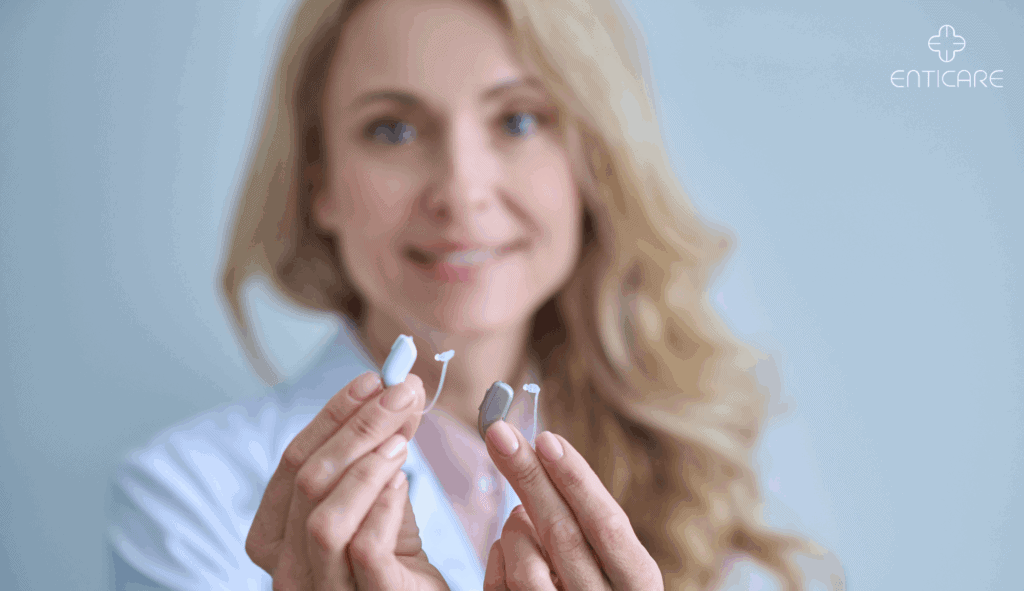

Understanding Hearing Loss: Why Professional Help Matters
Hearing loss varies from mild to profound and can result from many factors, making expert guidance essential. Here’s why seeking help matters.
Common Causes of Hearing Loss
Noise exposure, aging, genetics, and infections contribute to hearing loss. Professionals can diagnose the underlying cause and guide you to appropriate treatments.
Consequences of Ignoring Hearing Issues
Untreated hearing loss can affect cognitive health, social interactions, and well-being. Delaying seeking help may make symptoms worse, while timely intervention offers the best chance at effective treatment.
Signs You Need a Specialist
If you experience ringing in the ears, difficulty following conversations, or need the TV volume up, consider seeing a hearing aid specialist.
Types of Hearing Professionals
Navigating the world of hearing health can be daunting, especially with various specialists available to address different aspects of hearing loss. Understanding the roles of these hearing professionals can help you make informed decisions about your care.
Audiologists: Hearing Evaluation and Rehabilitation
Audiologists specialize in diagnosing and treating hearing and balance disorders, using various tests and tools to assess your hearing health.
When to See an Audiologist
Visit an audiologist for a hearing test if you suspect hearing loss or have persistent ringing. They conduct basic hearing tests to evaluate hearing thresholds and provide rehabilitation options, such as hearing aids.
Hearing Aids and Assistive Technology
Audiologists work with hearing aids, helping you select, adjust, and dispense hearing aids to improve your hearing. They may also recommend assistive devices for daily activities or suggest cochlear implants if hearing aids aren’t effective.
Balance and Dizziness Evaluations
Many audiologists assess and treat balance-related disorders, as inner ear issues can affect hearing and balance. If you feel dizzy or unsteady, an audiologist can help determine the cause.

Otolaryngologists (ENTs): Ear, Nose, and Throat Specialists
Otolaryngologists, or ENTs, diagnose and treat disorders affecting the ear, nose, and throat. Their expertise includes comprehensive medical and surgical care, particularly for ear-related issues.
Ear Infections and Blockages
ENTs address ear infections, earwax build-up, and other conditions that can temporarily impact hearing. They can treat diseases and safely remove earwax that may be causing blockages.
Hearing Loss from Medical Conditions
Chronic ear conditions, like otosclerosis or Meniere’s disease, require ENT expertise. ENTs may use medication, surgery, or referrals for specialized devices to manage hearing loss from these conditions.
Surgical Options for Hearing
ENTs perform surgeries to correct hearing issues when necessary, such as a stapedectomy for otosclerosis or a cochlear implant for severe hearing loss. Surgery offers a lasting solution for conditions not responsive to other treatments.
Otologists and Neurotologists: Specialized Ear Surgeons
Otologists and neurotologists have additional training beyond ENTs, specializing in complex ear and skull-based issues. Their expertise is essential for specific ear conditions.
When to See an Otologist or Neurotologist
Consider these specialists if you have chronic ear infections, severe ear trauma, or tumors affecting the ear. They handle conditions that require advanced surgical skills and in-depth knowledge of ear anatomy.
Managing Inner Ear Disorders
Conditions like vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma) and cholesteatoma can affect hearing and balance. Otologists and neurotologists often diagnose and treat these issues through surgery or other specialized care.
Advanced Surgical Procedures
Otologists and neurotologists perform delicate surgeries involving the inner ear and adjacent structures, such as cochlear implants or procedures to remove tumors near the ear. Their expertise reduces risks and enhances outcomes for complex ear conditions.
When to Seek Help: Identifying the Right Time and Specialist
Knowing when to consult a hearing specialist is critical to achieving better hearing and managing your hearing health effectively. Here’s how to decide when and who to see.
Persistent Symptoms
If you have experienced ringing, hearing loss, dizziness, or pressure in your ears for more than two weeks, consult a specialist. Audiologists can provide initial assessments, while ENTs or otologists may address underlying medical conditions.
Changes in Hearing or Balance
Sudden changes in hearing or balance can indicate serious issues. To prevent long-term damage, an ENT or neurotologist can assess urgent situations, such as sudden hearing loss or severe vertigo.
Hearing Aid Troubleshooting
Audiologists provide ongoing support for those with hearing aids. Visit your audiologist if you experience hearing instrument issues or an ENT if your hearing continues to worsen despite aids.
Take Control of Your Hearing Health
If hearing issues impact your life, consulting the right specialist can make all the difference. Don’t wait to start improving your hearing health Schedule an appointment with Enticare’s hearing experts today and take your first step toward a more transparent, more comfortable hearing.