Why Understanding Skin Conditions Matters
Have you ever wondered if the itchy patches on your skin are urticaria (hives) or dermatitis? While these conditions share similarities, their causes, symptoms, and treatments differ. Knowing the difference helps you manage symptoms effectively and seek proper treatment. In this guide, you’ll discover what sets these conditions apart and learn how to care for your skin.
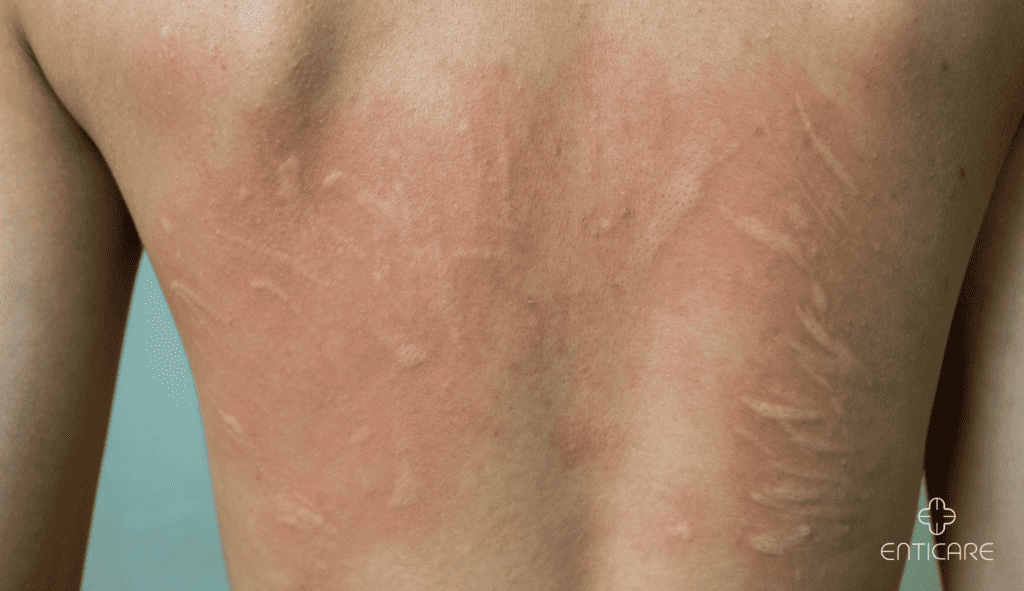
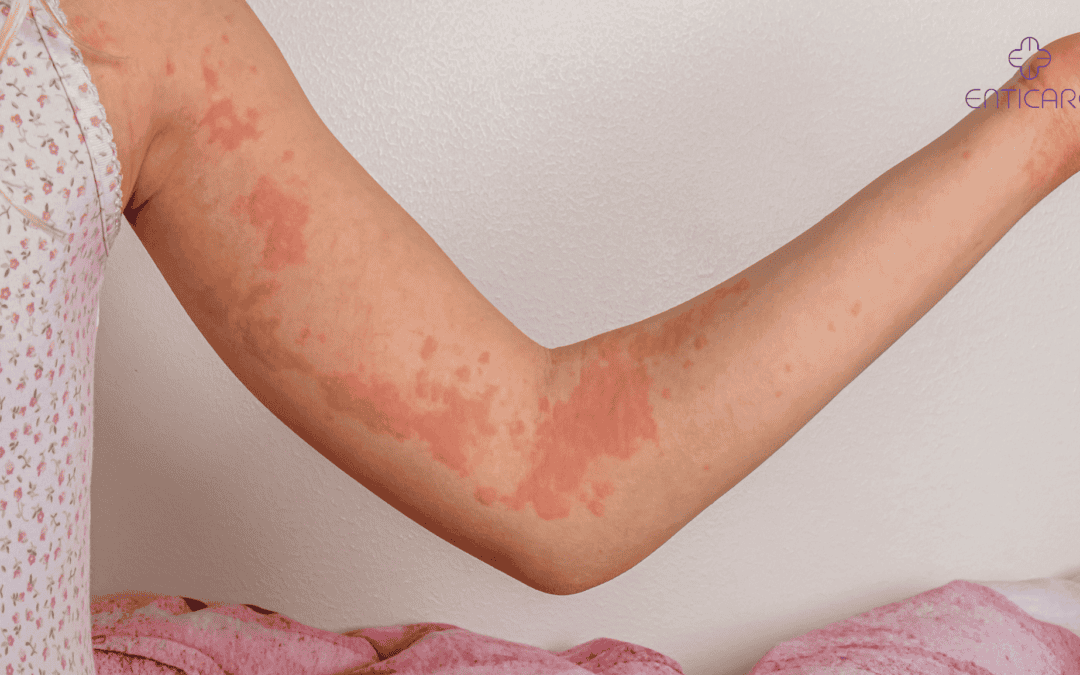
What Is Urticaria?
Types of Urticaria: Acute and Chronic Urticaria
- Acute and Chronic Urticaria: Urticaria can be classified into acute and chronic forms. Acute urticaria symptoms appear suddenly and typically last less than six weeks, often triggered by allergens or illnesses. Chronic urticaria symptoms persist for six weeks or more and may not be directly related to allergies, necessitating further medical management.
- Physical Urticaria: Triggers include cold, heat, pressure, or exercise.
Common Triggers
- Allergens: Foods, medications, or insect stings often cause hives.
- Environmental Factors: Pollen, sunlight, or water exposure can act as triggers.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress may worsen symptoms.
Symptoms and Duration
- Appearance: Raised, red, or pale welts that may merge to form larger patches.
- Itching: Intense itching accompanies most cases.
- Duration: Acute urticaria, also known as acute hives, resolves within 24 hours, while chronic cases linger longer.
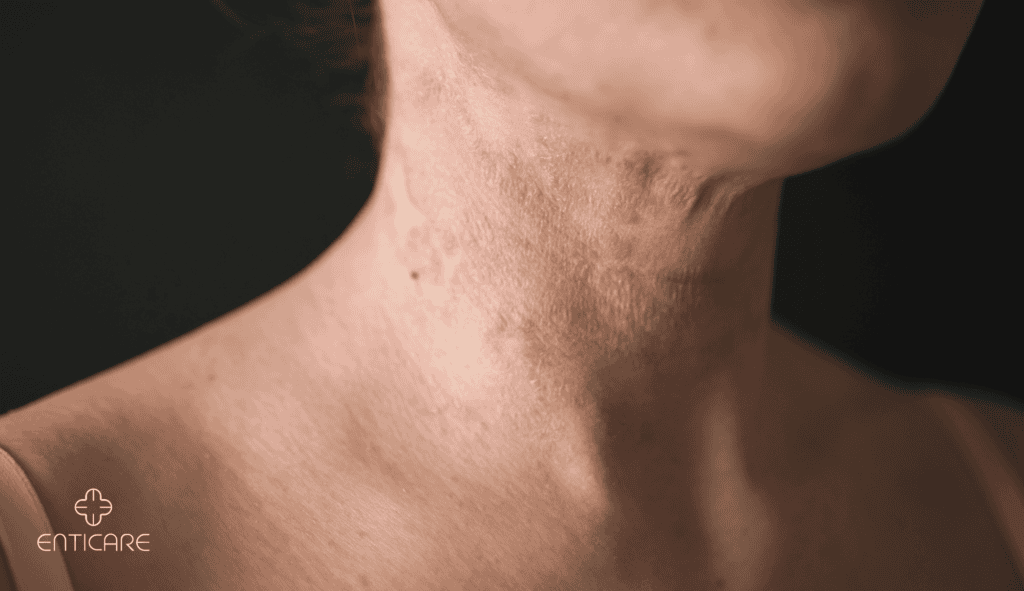
What Is Dermatitis?
Types of Dermatitis: Atopic Dermatitis
- Atopic Dermatitis: Also known as eczema, it often starts in childhood and flares periodically.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by irritants or allergens touching the skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects oily areas like the scalp and face, often linked to yeast overgrowth.
Common Triggers
- Irritants: Soaps, detergents, or chemicals in skincare products.
- Allergens: Metals like nickel, fragrances, or specific plants like poison ivy.
- Food Allergy: Certain foods can trigger allergic skin reactions and are linked to conditions like eczema and atopic dermatitis.
- Environmental Factors: Dry air, extreme temperatures, or seasonal changes.
Symptoms and Duration
- Appearance: Red, scaly patches, often accompanied by blisters or cracking.
- Itching: Persistent itchiness, especially during flare-ups.
- Duration: Dermatitis tends to be chronic but can improve with proper treatment.
Critical Differences Between Urticaria and Dermatitis
Appearance, Texture, and Itchy Skin
- Urticaria: Raised, smooth welts that often disappear within hours.
- Dermatitis: Scaly, rough patches that may blister or ooze.
Onset and Duration
- Urticaria: Appears suddenly and resolves quickly, though chronic cases persist.
- Dermatitis: Develops gradually, with symptoms that come and go over time.
Underlying Causes
Urticaria: Often linked to allergic skin conditions, physical stimuli, or stress.
Dermatitis: Triggered by irritants, allergens, or genetic predispositions like eczema.
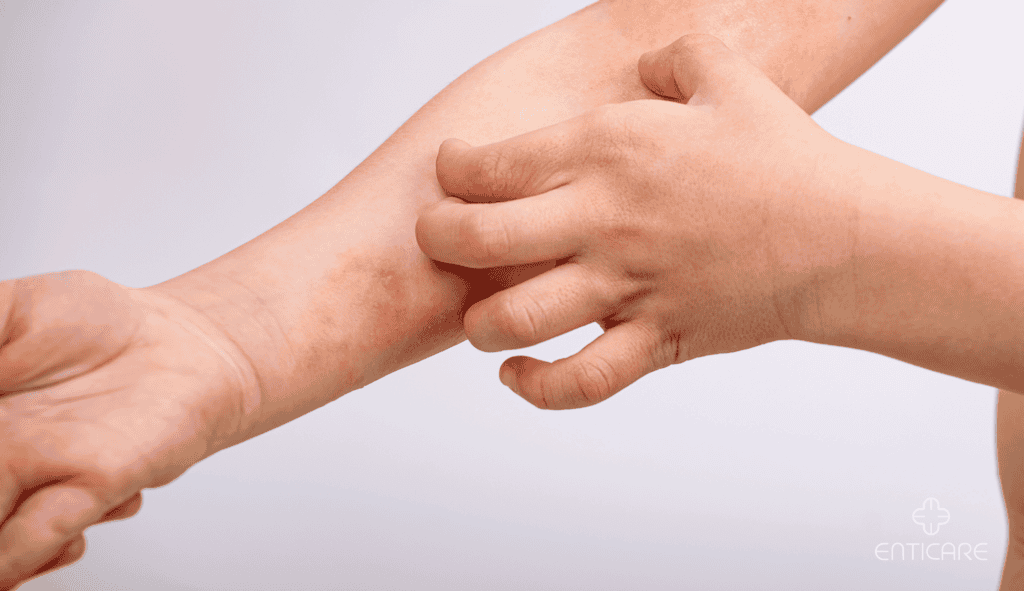

Effective Treatments for Urticaria and Dermatitis
Medical Treatments: Topical Corticosteroid Creams
- Antihistamines: Reduce itching and swelling for urticaria.
- Topical Corticosteroid Creams: Calm inflammation in dermatitis by reducing redness and itching.
- Immunosuppressants: Used for severe or chronic cases of both conditions.
Home Remedies
- Cold Compresses: Soothe itching and reduce swelling in urticaria.
- Moisturizers: Hydrate and repair the skin barrier for dermatitis.
- Oatmeal Baths: Relieve irritation and itchiness for both conditions.
Prevention Strategies
- Identify Triggers: Keep a symptom diary to track allergens or irritants.
- Use Gentle Products: Choose hypoallergenic skincare and detergents.
- Stay Consistent with Treatment: Follow a dermatologist’s plan to minimize flare-ups.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing skin conditions can be complex due to the similarity of symptoms across different conditions. A thorough diagnosis typically involves several steps:
- Medical History: A detailed medical history helps identify any previous skin conditions, allergies, and medications that might be relevant.
- Physical Examination: A careful examination of the skin can reveal signs of inflammation, dryness, or other abnormalities.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests or skin scrapings may be conducted to rule out other conditions or confirm a diagnosis.
- Allergy Testing: Identifying specific allergens through testing can help pinpoint triggers and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
Key Takeaways
- Urticaria presents as smooth, raised welts, while dermatitis appears as scaly, rough patches.
- Urticaria resolves quickly but may persist in chronic cases, while dermatitis tends to be ongoing.
- Effective treatments include antihistamines, topical steroids, and lifestyle adjustments.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention:
- Severe itching or burning sensation on the skin
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- Dizziness or fainting
- Fever or chills
- Pus or discharge from the skin
- Skin that is warm to the touch or has a foul odor
Additionally, if your skin condition is not responding to treatment or you are experiencing frequent flare-ups, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for proper management and relief.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Don’t let itchy skin conditions disrupt your life. Whether you’re dealing with urticaria or dermatitis, proper care and expert advice can help. At Enticare, our specialists provide personalized treatment plans for your unique skin needs. Schedule your appointment today by visiting Enticare and take the first step toward healthier, happier skin.