Allergies affect millions worldwide, causing symptoms that range from mild discomfort to life-threatening reactions. Allergy skin tests are one of the methods used to diagnose allergic conditions by exposing the skin to various allergens. Identifying the specific allergens triggering symptoms is essential for effective management. Allergists use a variety of tests to pinpoint the allergens affecting you. In this blog, we’ll explore seven different types of allergy tests and explain how each can help identify and manage allergies.
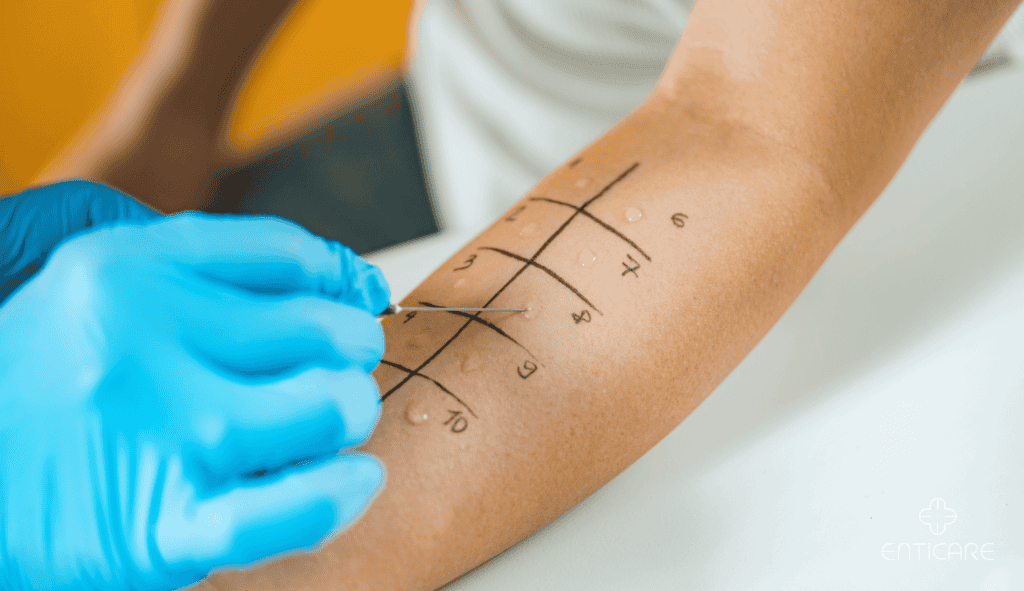
Skin Prick Test: A Simple and Common Allergy Test
Allergy skin testing, including the skin prick test, is one of the most commonly used procedures for identifying specific allergens. This method gives results quickly and efficiently.
How It Works
The allergist places a tiny drop of potential allergens on your skin, usually on the forearm or back, and gently pricks the skin to allow a small amount of the allergen to enter. This allergy skin test is then monitored for signs of an allergic reaction, such as redness, swelling, or a histamine response.
What It Detects
Skin prick tests help identify allergies to airborne particles (like pollen), foods, pet dander, environmental allergens, and even certain medications. This test is often the first step in assessing a range of allergies.
Benefits and Limitations
Skin prick tests are quick, relatively painless, and provide immediate results. However, this test might not suit people with severe skin conditions or specific drug allergies. Additionally, there is a potential risk of a severe allergic reaction during the test.
Intradermal Skin Test: Enhanced Sensitivity for Specific Allergens
Intradermal skin testing offers enhanced sensitivity, making it ideal for detecting specific allergens.
Testing Procedure
For this test, the allergist injects a small amount of allergen extract just under the skin’s surface. This deeper injection increases sensitivity, especially for certain allergens, such as insect venom or drug reactions.
When to Use It
Intradermal skin tests are typically used when a skin prick test does not produce a conclusive result. They are especially useful for identifying insect venom allergies or drug reactions that require a higher sensitivity.
Potential Risks
While generally safe, intradermal tests may increase the risk of a stronger reaction, so allergists closely monitor patients during the test.
However, it is essential to note that while intradermal skin tests are helpful, they alone do not diagnose allergies and must be interpreted alongside the individual’s medical history and symptoms.
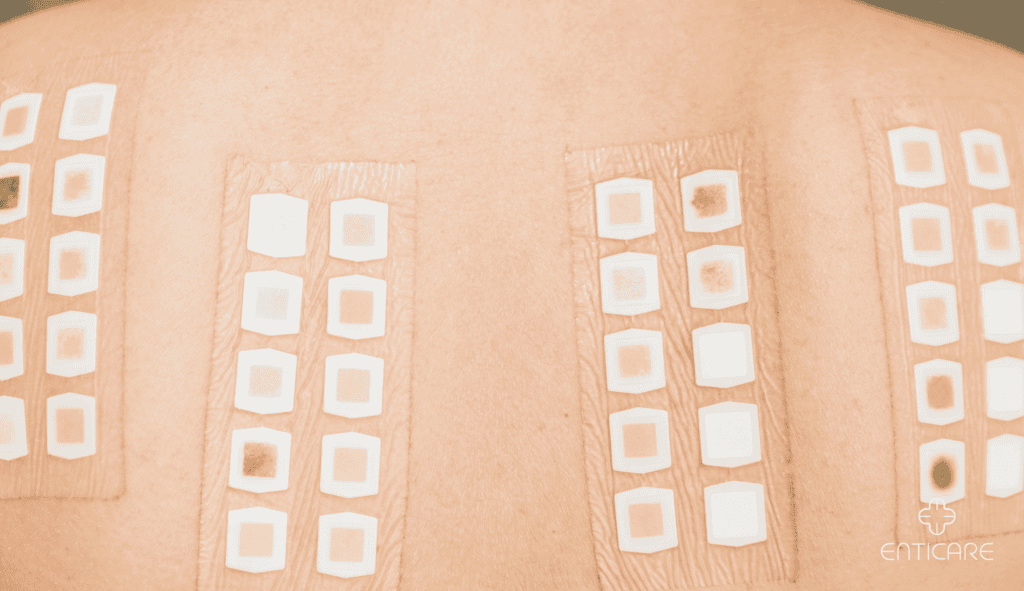

Patch Test: Ideal for Diagnosing Contact Dermatitis
Patch testing helps pinpoint allergens that cause delayed reactions on the skin, a common issue in contact dermatitis.
Procedure and Timing
The allergist places patches with small amounts of potential allergens on your back or arm. The patches remain in place for 48 hours, allowing time to observe delayed hypersensitivity reactions to common allergens in cosmetics, soaps, or metals.
Typical Allergens Detected
Patch tests often detect contact allergens such as metals (like nickel), fragrances, dyes, and preservatives—common causes of contact dermatitis. This test is beneficial for individuals experiencing unexplained skin rashes.
Pros and Cons
Patch testing helps identify allergens not detected by immediate skin tests, making it particularly useful for diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis. However, multiple visits are required for patch placement, removal, and evaluation. Interpreting patch test results in conjunction with a patient’s medical history is crucial to accurately identify allergic triggers and inform treatment plans.

Blood Test (ImmunoCAP or RAST): Measuring Immune Response
Blood tests like the ImmunoCAP or RAST test measure serum IgE levels to provide a different approach to allergy testing. They measure the immune system’s reaction to specific allergens.
How Blood Tests Work
The allergist draws a small blood sample and sends it to a laboratory to measure immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. Elevated IgE levels often indicate an allergic reaction to specific allergens.
Advantages of Blood Testing
Blood tests are useful for patients who cannot undergo skin testing, such as those with severe skin conditions or at risk of anaphylaxis. They also allow for the testing of multiple allergens at once without exposure.
Limitations
Blood tests usually take longer to provide results and may be less sensitive than skin tests. However, they remain a valuable option for certain patients.
Food Challenge Test: Pinpointing Food Allergies with Precision
The food challenge test, also known as an oral food challenge, accurately diagnoses specific food allergies.
What to Expect During the Test
Under medical supervision, the patient ingests small, controlled amounts of a suspected allergen, gradually increasing the dose while monitoring for any signs of an allergic reaction. This test is often conducted in a clinic or hospital to monitor for any signs of an allergic reaction and assess oral tolerance.
Why It’s Effective
Food challenge tests provide accurate results, making them one of the most reliable ways to confirm food allergies. This test is essential for seeking clarification on a potential food allergy before making dietary changes.
Safety Precautions
Due to the potential for severe reactions, allergists closely monitor patients and take immediate action if necessary, ensuring the procedure is effective and safe.
Spirometry and Lung Function Tests: Identifying Allergy-Induced Asthma
Allergies often impact the respiratory system, leading to asthma or other breathing difficulties. Spirometry and lung function tests help diagnose asthma and assess lung health.
How Spirometry Works
The test measures the amount of air you can exhale and the speed at which you exhale. Allergists may perform this test before and after administering a bronchodilator to observe any improvements in lung function.
What It Detects
Spirometry and other lung function tests detect asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other conditions where allergens play a role. By assessing lung function, allergists can recommend treatments that help you breathe easier.
Benefits for Allergy Patients
Lung function tests allow for a targeted treatment approach for people with respiratory issues related to allergies. This helps relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Component Testing: Advanced Allergy Analysis for Detailed Insight
Component testing provides in-depth information on allergens, focusing on specific proteins within allergens rather than just identifying the allergen itself.
How It Works
Blood samples are analyzed for specific molecular allergens within an allergen. This detailed analysis can help differentiate between mild and severe reactions, especially for food allergies.
Applications of Component Testing
This test often proves helpful in cases of peanut or milk allergies, where specific proteins trigger reactions. Knowing which proteins cause reactions helps allergists design safer, personalized management plans.
Benefits of Component Testing
Component testing offers greater insight, allowing allergists to differentiate between cross-reactive and true allergens. Based on this detailed analysis, patients receive targeted advice.
Take the First Step Toward Allergy Relief
Allergy testing provides essential insights to help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. If you’re experiencing allergy symptoms, it’s time to schedule an appointment with an allergist. Book a consultation with Enticare’s allergy specialists here and get started on a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.