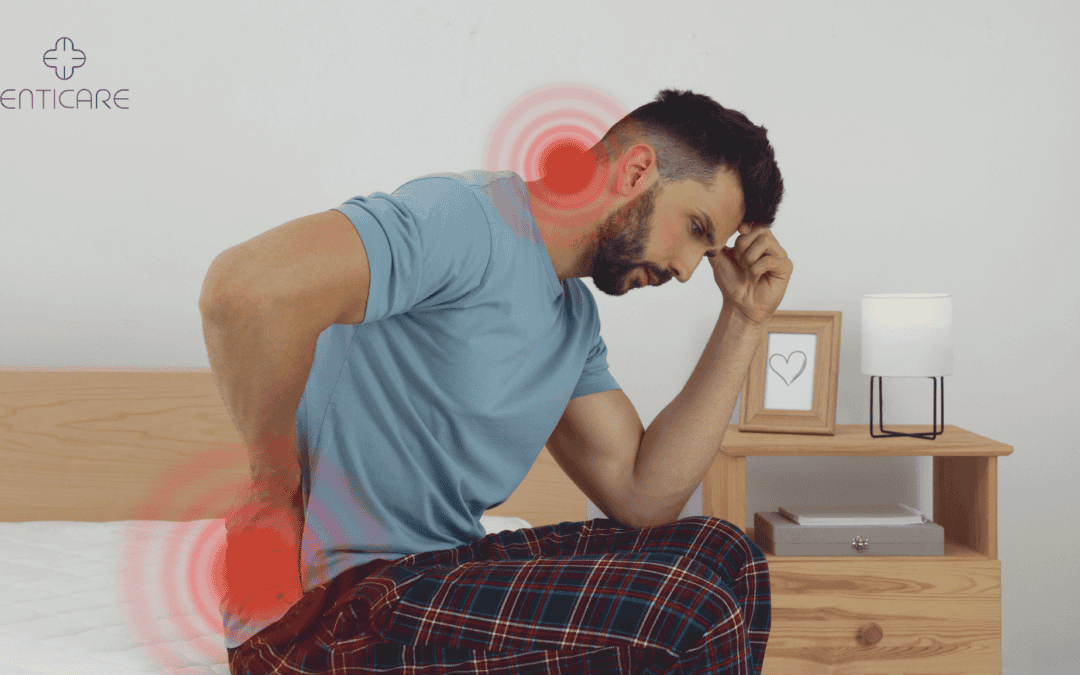
Sleep apnea and back pain are two health concerns that many people face, but they rarely connect to one another. Sleep fragmentation, a common consequence of sleep apnea, significantly impacts sleep quality and can exacerbate back pain. However, recent studies suggest a strong link between the two conditions, particularly how sleep apnea can lead to poor quality sleep, which may result in chronic pain such as back pain. If you suffer from both sleep apnea and chronic back pain, this connection could offer important insights into improving your overall health and quality of life. Understanding how these two conditions influence each other can be the key to effective treatment.
In this blog, we will dive deep into the relationship between sleep apnea and back pain, how they impact each other, and what you can do to find relief.
What Is Sleep Apnea? Understanding the Condition
Before exploring how sleep apnea links to back pain, it’s crucial to understand what sleep apnea is and how it affects your body. Severe obstructive sleep apnea, in particular, can significantly impact overall health and quality of life. Sleep apnea disrupts your breathing while you sleep by affecting the upper airway, leading to numerous health complications.
Types of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea comes in two main types: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and central sleep apnea (CSA). OSA, the most common type, occurs when the throat muscles relax too much, causing airway obstruction and blocking airflow. Severe obstructive sleep apnea can significantly impact overall health and quality of life, often requiring additional treatments such as CPAP machines and a multifaceted approach, including exercise and chiropractic care. CSA, on the other hand, happens when the brain fails to send proper signals to the muscles that control breathing. Both forms cause fragmented sleep, leading to various health issues.
Common Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Loud snoring, choking or gasping for air during sleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, and morning headaches are among the most common symptoms of sleep apnea. Some individuals may also experience neck pain as a consequence of sleep apnea. If left untreated, it can increase the risk of serious conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
How Sleep Apnea Disrupts Sleep
The repeated interruptions in breathing cause sleep fragmentation, leading sleep cycles to break down. As a result, the body spends less time in the deep, restorative phases of sleep. Without proper rest, the body cannot fully recover, leading to muscle tension and stress on various parts, including the back.

The Connection Between Sleep Apnea and Back Pain
Sleep apnea and back pain might seem like unrelated issues, but they can exacerbate one another in several ways. Sleep apnea can disrupt ‘sleep architecture,’ the overall structure of sleep, leading to fragmented sleep and contributing to back pain. Poor quality sleep due to sleep apnea can worsen chronic pain, while certain sleeping positions can aggravate both conditions.
Poor Sleep Quality Increases Sensitivity to Pain
When sleep apnea disrupts your rest, it leads to poor quality sleep, causing the body to struggle to repair muscles and tissues. This lack of recovery can heighten sensitivity to pain, especially in areas like the back. Studies show that poor sleep leads to a heightened response to pain, lowering the pain threshold and increasing the likelihood of chronic back pain worsening over time.
Sleeping Position and Spinal Alignment
Many people with sleep apnea sleep on their backs because they may feel more comfortable. However, some individuals may experience neck pain as a consequence of sleep apnea. Unfortunately, back sleeping can cause the tongue and soft tissues of the throat to collapse into the airway, worsening sleep apnea symptoms. Additionally, this position may strain the lower back, leading to increased pain. Side sleeping, while beneficial for sleep apnea, may still contribute to back pain if not supported properly with a good mattress and pillows. Proper side sleeping can also promote better spinal alignment, reducing discomfort and improving overall sleep quality.
Sleep Deprivation and Muscle Tension
Sleep disturbance leads to physical stress on the body, which can cause muscle tension. When muscles are stiff and tense, especially in the back, you are more likely to experience discomfort or injury. In turn, this creates a cycle where sleep apnea makes back pain worse, and back pain further disrupts sleep.
The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in Sleep Apnea
Pro-inflammatory cytokines are key players in the development and progression of sleep apnea. These molecules, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), are produced in response to inflammation and can significantly impact sleep apnea symptoms.
Research indicates that individuals with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) have elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in their bloodstream compared to those without the condition. These cytokines contribute to inflammation in the upper airway, causing it to narrow and obstruct breathing during sleep. This not only exacerbates sleep apnea symptoms but also leads to poor sleep quality and sleep disturbances.
Moreover, the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines is closely linked to chronic pain, a common issue for those with sleep apnea. Elevated levels of these cytokines can increase pain sensitivity, leading to conditions such as chronic back pain and neck pain. This creates a vicious cycle where sleep apnea leads to increased inflammation, which in turn worsens pain symptoms and further disrupts sleep.
Treating sleep apnea effectively can help break this cycle. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, a common treatment for severe obstructive sleep apnea, has been shown to reduce levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby improving sleep quality and reducing chronic pain. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as weight loss and regular exercise can help lower inflammation and alleviate sleep apnea symptoms.
Understanding the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in sleep apnea underscores the importance of comprehensive treatment plans. By addressing both the sleep disorder and the associated inflammation, individuals can achieve better sleep quality and relief from chronic pain.
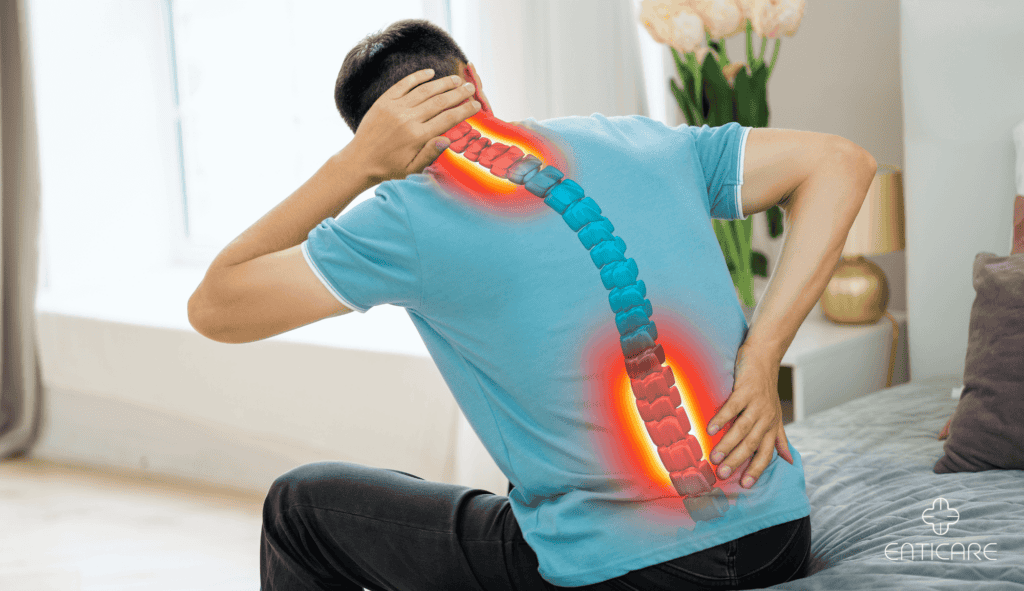
The Role of Sleep Disturbances in Chronic Pain
Sleep disturbances play a significant role in chronic pain, often exacerbating pain symptoms and reducing the effectiveness of pain management treatments. Research has shown that sleep disturbances, such as insomnia and sleep apnea, are common among individuals with chronic pain. In fact, studies have found that up to 70% of individuals with chronic pain experience sleep disturbances. This high prevalence underscores the importance of addressing sleep issues as part of a comprehensive pain management plan.
Impact of Interrupted Sleep on Pain Perception
Interrupted sleep can significantly impact pain perception, making individuals more sensitive to pain. When sleep is disrupted, the body’s natural pain-relieving mechanisms are impaired, leading to increased pain sensitivity. Additionally, sleep disturbances can lead to increased inflammation, which can further exacerbate pain symptoms. This creates a vicious cycle where poor sleep leads to more pain, and more pain leads to even worse sleep.
Long-term Effects of Sleep Deprivation
Chronic sleep deprivation can have long-term effects on pain management, leading to increased pain sensitivity, decreased pain tolerance, and reduced quality of life. Over time, sleep deprivation can increase the risk of developing chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia and chronic back pain. Addressing sleep issues early on is crucial for preventing these long-term consequences and improving overall well-being.
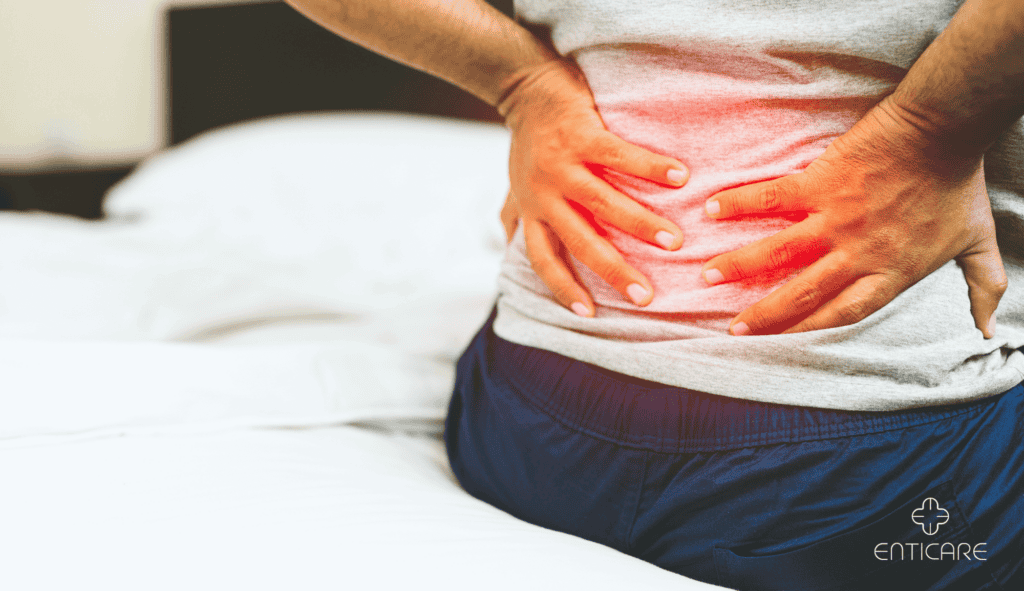
How Untreated Sleep Apnea Can Worsen Back Pain
Ignoring sleep apnea doesn’t just worsen your quality of sleep—it can lead to more severe back pain as well due to oxygen deprivation. Severe obstructive sleep apnea can significantly impact overall health and quality of life, often necessitating additional treatments such as CPAP machines. Here’s why treating your sleep apnea can help reduce or even eliminate your back pain.
Chronic Inflammation
Untreated sleep apnea often leads to chronic inflammation in the body due to the inflammatory response triggered by interrupted sleep and oxygen deprivation. Some individuals may also experience neck pain as a consequence of sleep apnea. Inflammation can manifest in various ways, including muscle and joint pain, particularly in the back. Addressing sleep apnea helps reduce inflammation, potentially alleviating back pain.
Weight Gain and Stress on the Spine
Sleep apnea and weight gain often go hand in hand, leading to poor-quality sleep. When people don’t sleep well, their metabolic rate slows, and they often feel too tired to exercise, leading to weight gain. Extra weight puts additional stress on the spine, worsening any existing back pain. Treating sleep apnea can help regulate sleep patterns and metabolism, reducing the risk of weight gain and spinal stress.
Postural Problems During the Day
Sleep apnea causes fatigue, drowsiness, and sleep disturbance throughout the day. People with untreated sleep apnea may have poor posture while sitting or standing, which can contribute to back pain. As energy levels drop, they may slouch or sit in awkward positions that strain the spine. Correcting sleep apnea can boost energy levels and improve posture, which can relieve back pain by enhancing ergonomics.
Identifying and Treating Undiagnosed Sleep Disorders
Identifying and treating undiagnosed sleep disorders is crucial for effective pain management. A sleep study is essential in diagnosing sleep disorders, providing valuable insights into sleep patterns and identifying issues like sleep apnea. Sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome, can significantly impact pain symptoms and reduce the effectiveness of pain management treatments. Many individuals with chronic pain may have undiagnosed sleep disorders that are contributing to their pain.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of sleep disorders are essential for preventing long-term consequences, such as chronic pain and reduced quality of life. Healthcare providers should consider sleep disorders as a potential underlying cause of chronic pain and take a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment, utilizing various diagnostic tools. By addressing sleep disorders early, individuals can improve their sleep quality, reduce pain symptoms, and enhance their overall quality of life.
By understanding the link between sleep disturbances and chronic pain and by identifying and treating undiagnosed sleep disorders, individuals can take significant steps toward better pain management and improved overall health. If you suspect that a sleep disorder may be contributing to your chronic pain, consult with a healthcare provider to explore potential treatment options.
Treating Sleep Apnea to Relieve Back Pain
Fortunately, treating sleep apnea can significantly improve both your sleep quality and your back pain. Severe obstructive sleep apnea, in particular, can have a profound impact on overall health and quality of life, necessitating a multifaceted approach to treatment. A combination of lifestyle changes, medical devices, and professional treatments can provide relief.
CPAP Therapy
The most common and effective treatment for sleep apnea is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy. Severe obstructive sleep apnea, in particular, often requires CPAP therapy to manage the condition and improve overall health and quality of life. A CPAP machine delivers a steady stream of air through a mask, keeping your airways open while you sleep. This ensures you get enough oxygen, reduces sleep interruptions, and allows your body to heal properly, which can lead to a reduction in back pain.
Sleep Position Adjustments
For both sleep apnea and back pain, changing your sleep position can make a significant difference. Additionally, individuals may experience neck pain as a consequence of sleep apnea. Sleeping on your side can reduce airway obstruction and improve spinal alignment. Using a body pillow or wedge pillow can provide support for the back and ensure a comfortable sleep posture.
Weight Management and Exercise
Losing weight is one of the most effective ways to reduce the severity of sleep apnea, which often leads to poor quality sleep, and relieve pressure on the back. Regular exercise, especially activities that strengthen the core muscles and back muscles, can improve both conditions. By focusing on maintaining a healthy weight, you can improve your sleep apnea and experience relief from back pain.
When to See a Doctor for Sleep Apnea and Back Pain
If you suspect that sleep apnea is contributing to your back pain, it’s essential to seek medical advice. Severe obstructive sleep apnea can significantly impact overall health and quality of life, necessitating treatments like CPAP machines and a multifaceted approach, including exercise and chiropractic care. Untreated sleep apnea can lead to long-term complications, including worsening pain and fatigue. Consult a sleep specialist to get a comprehensive evaluation and appropriate treatment plan.
Persistent Symptoms
If you experience loud snoring, frequent awakenings, or chronic daytime fatigue alongside your back pain, it may be time to see a doctor. Individuals with sleep apnea may also experience neck pain, which can be alleviated with effective treatment. Sleep apnea symptoms, when left untreated, can worsen over time and contribute to a range of other health issues.
Severe Back Pain
Back pain that doesn’t improve with lifestyle changes or at-home treatments requires professional evaluation. Your doctor can determine whether your pain stems from poor-quality sleep or another underlying condition.
Customized Treatment Plans
A sleep specialist can create a customized treatment plan that addresses both your sleep apnea and back pain. For those suffering from severe obstructive sleep apnea, a comprehensive approach is crucial to manage the condition effectively. By tackling both issues simultaneously, you can improve your sleep quality and alleviate chronic pain.
Take the First Step Toward Better Sleep and Pain Relief
Don’t let sleep apnea and back pain continue to affect your quality of life. Severe obstructive sleep apnea can significantly impact your overall health and quality of life, making it crucial to seek appropriate treatment. By addressing both conditions together, you can achieve better sleep, reduced pain, and an overall improvement in your well-being.
If you think sleep apnea might be contributing to your back pain, schedule an appointment with one of our specialists today. Click here to start your journey to better health!

